The Strength of Tectonic Plates Caused the Unique Shape of the Tibetan PlateauUpdate time:09 05, 2017
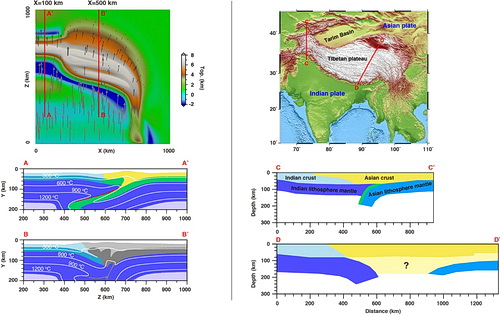
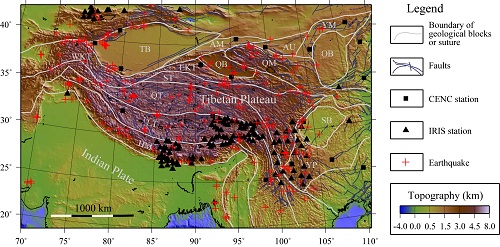
An aerial photography of Tibetan Plateau(Image form blog.sina.com.cn) The Tibetan plateau has a narrow western part and a broad eastern part, but the mechanisms that produced this structure are unclear. A recent study by Dr. CHEN Lin from IGG, and his collaborators demonstrates that the unique shape and complex deep structure of the Tibetan plateau may be largely controlled by the strength heterogeneity of the tectonic plates during collision. These new findings were published in Nature Communications. The Tibetan plateau, which formed by the convergence of the Indian and Asian tectonic plates, dwarfs Earth’s other mountain ranges in height and breadth. Most other mountain ranges look like narrow ridges, while the Tibetan plateau appears like a broad and asymmetrical scab surrounded by craggy peaks. For example, the western side of the Tibetan plateau is relatively narrow and its eastern side is very broad, and recent seismic investigations also reveal that the subsurface structure of the Tibetan plateau changes dramatically along the collisional zone, which existing models have failed to explain. Why does the Tibetan plateau vary laterally so much? To address the above question, CHEN and his co-authors looked at what happens when the two colliding tectonic plates are made from rocks with different strength. A series of 3-D thermo-mechanical continental collision models were used to explore this idea. The researchers first looked at two scenarios: a weak Asian plate and a strong Asian plate, while maintaining a strong incoming Indian plate in both models. They found that the strong Asian plate led to a narrow orogen, but the weak Asian plate resulted in a broad orogenic plateau. They then ran a third model, which was a composite of the strong and weak Asian plate models. An Asian plate with a strong western side and a weak eastern side produces a continental plateau very similar to the present-day Tibetan plateau in shape. This model also predicts some of the complex subsurface structures revealed from seismic investigations at the Tibetan plateau. Lithospheric strength heterogeneities are common in continental crust. Therefore, these findings provide new insights into the development of mountain chains and plateau topography around collisional margins. This study was done in collaboration with Dr. Fabio Capitanio from Monash University, Dr. Lijun Liu from University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Prof. Taras Gerya from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB18000000), by the National Key Research and Development Project (2016YFC0600406, 2016YFC0600101), and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41474084, 41490610).
Figure Comparison between the composite model predictions (left) and the observations from the Tibetan plateau (right).
|
Contact
CHEN Lin State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, IGGCAS Phone: +86-10-82998527 E-mail: chenlin@mail.iggcas.ac.cn Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close