Globally optimized finite-difference extrapolator for strongly VTI mediaUpdate time:07 12, 2012
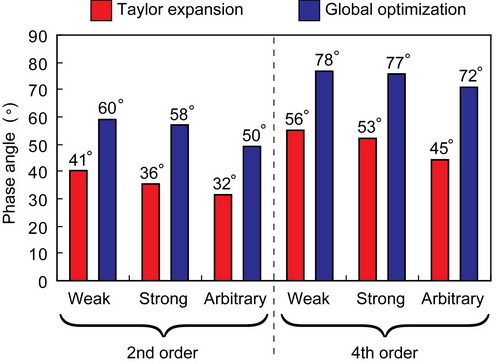
Vice Professor ZHANG Jinhai and his teacher YAO Zhenxing develop an implicit FD method using the analytic Taylor-series expansion and use a global optimization scheme to improve its accuracy for wide phase angles. Their global optimization scheme guarantees the accuracy for various possible ranges of anisotropy parameters, no matter how strong the anisotropy is. For the globally optimized second-order FD method, the accurate phase angle is up to 58°, and the increase is about 18°–22°. For the globally optimized fourth-order FD method, the accurate phase angle is up to 77°, and the increase is about 22°–27°.
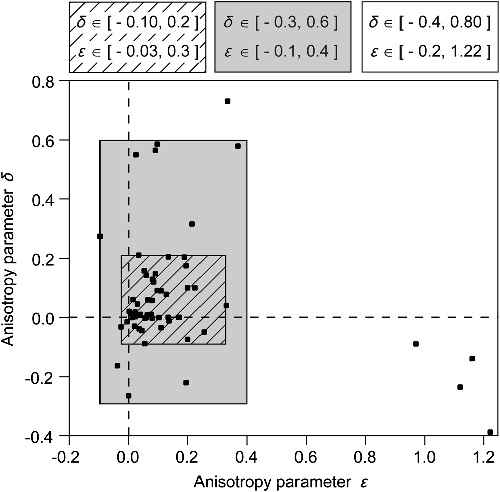
Figure 1. Scattering graph of Thomsen parameters of measured anisotropy in sedimentary rocks. (Image by ZHANG) Figure 2. The improvement of accurate phase angle due to using our global optimization scheme for various cases. (Image by ZHANG) Figure 3. Relative error versus phase angle for strong anisotropy using the fourth-order FD method. (Image by ZHANG) Zhang and Yao. Globally optimized finite-difference extrapolator for strongly VTI media. Geophysics. 2012, 77, S125-S135 (Download Here)
|
Contact
Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close