Intralithospheric mantle structures recorded continental subductionUpdate time:03 30, 2012
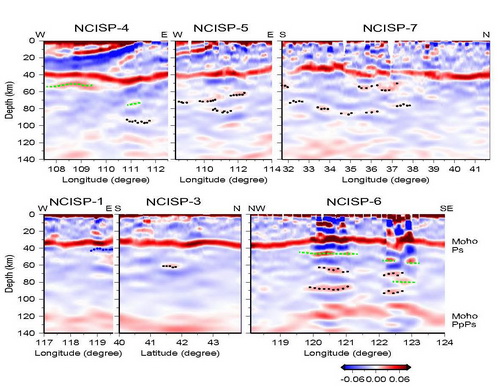
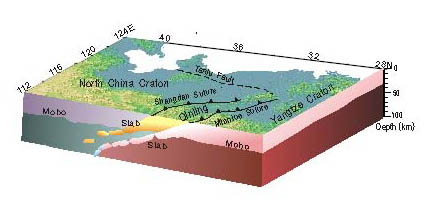
Professor ZHENG Tianyu and her team investigate the intralithospheric mantle (ILM) structures beneath the North China Craton (NCC) by the seismic imaging with over 16,000 high-quality receiver functions from 255 broadband stations. These images are created for six profiles spanning different tectonic units in the NCC. Their imaging results reveal (1) a homogenous lithospheric mantle in the western NCC, (2) intermittent and juxtaposed velocity interfaces in the ILM beneath the southern NCC, and (3) local high-velocity and lower-velocity volumes in the ILM beneath the eastern NCC. In addition, the lower crust beneath the southern NCC is thin, and the Moho dips northward, which present evidence of the Yangtze craton subduction beneath the NCC. The imaged high-velocity volumes in the ILM beneath the southern NCC were interpreted as a subduction remnant in the uppermost mantle, which reveal a flat subduction channel resulting from the continent-continent collision between the NCC and the Yangtze craton. The homogeneous ILM beneath a Paleoproterozoic amalgamation zone in the NCC implies that the remnants of the lithosphere that were subducted before 1.8 Ga might have sunk into the deeper mantle.
Figure 1. The common conversion point (CCP) stacking receiver function images of the crust and lithospheric mantle along profiles. (Image by ZHENG)
Figure 2. Cartoon depicting the intralithospheric mantle structure associated with the continental subduction. (Image by ZHENG) Zheng et al. Intralithospheric mantle structures recorded continental subduction, Journal of Geophysical Research. 2012, 117, B03308, doi:10.1029/2011JB008873 (Download Here)
|
Contact
Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close