Quantification of hematite from the visible diffuse reflectance spectrum: effects of aluminium substitution and grain morphologyUpdate time:05 16, 2011
Professor LIU Qingsong and his team investigate systematically the effects of Al substitution on the visible diffuse reflectance spectrum (DRS) of hematite by using several sets of synthetic samples. They find that the position and amplitude of the characteristic absorption band of hematite (estimated from the first- and second-order derivative curves of the Kubelka-Munk remission function spectrum derived from the DRS) is significantly affected by the degree of Al substitution as well as by sample grain morphology. Therefore, there are ambiguities in quantifying the degree of Al substitution and the mass concentration of hematite using DRS. Liu et al. Quantification of hematite from the visible diffuse reflectance spectrum: effects of aluminium substitution and grain morphology. Clay Minerals, 2011, 46: 137-149 (Download Here)
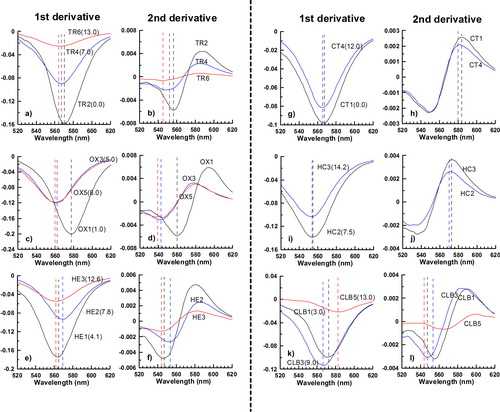
FIG. 1 The first- and second-order derivatives of the K-M functions for the first set of hematite samples. (Image by LIU)
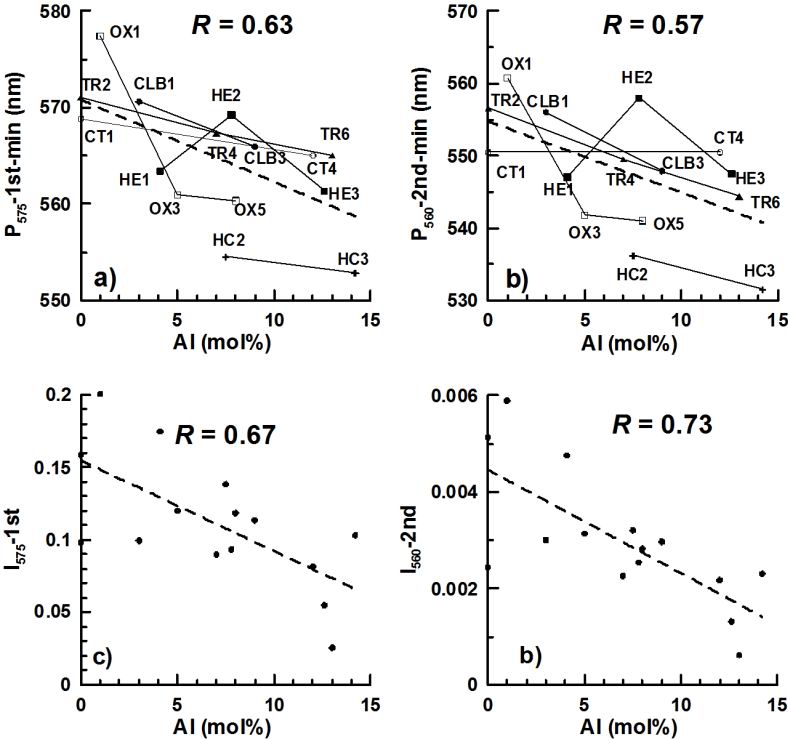
FIG. 2 Correlation between the DRS proxies and the Al substitution for the first set of hematite samples. (Image by LIU)
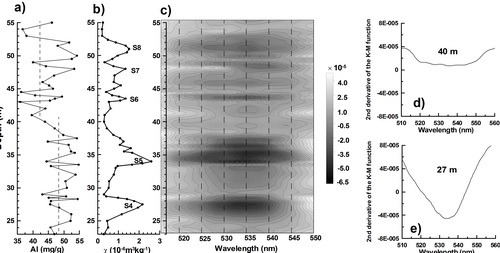
FIG. 3 Depth variations of total Al and magnetic susceptibility for the bulk samples. (Image by LIU)
|
Contact
Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close