On the selection of reference velocities for split-step Fourier and generalized-screen migration methodsUpdate time:02 25, 2011
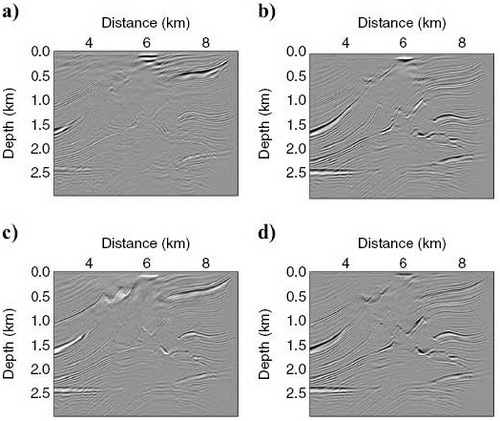
Migration results on Marmousi model. Professor CHEN Jingbo researches on the selection of reference velocities for split-step Fourier and generalized-screen migration methods. This paper has been published on Geophysics. Split-step Fourier and generalized-screen migration methods are approximations with separation of variables to the one-way wave operator, in which the separation of space and wavenumber variables makes it possible to use the discrete fast Fourier transform to achieve computational efficiency. Both methods require the selection of reference velocities. Different choices of reference velocities lead to different velocity perturbations, and the smaller the velocity perturbations, the better the final image quality. The benefits of selecting amore representative reference velocity for the split-step Fourier method can be extended to the eneralized-screen method by removing the limitation on the reference velocity for the generalized-screen method. Numerical experiments on the Marmousi model demonstrate the improvement of imaging by using an average velocity instead of the minimum velocity as the reference velocity for the generalized-screen method. Chen et al. On the selection of reference velocities for split-step Fourier and generalized-screen migration methods. Geophysics, 2010, 75(6): S249-S257(Download Here)
|
Contact
Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close