Highlight 2009-023Update time:09 04, 2009
Journal of Quaternary Science,2009,24:547 - 551
Comparative analysis between a proxy-based climate reconstruction and GCM-based simulation of temperatures over the last millennium in China Ming Tan 1 *, Xuemei Shao 2, Jian Liu 3, Binggui Cai 1 Abstract
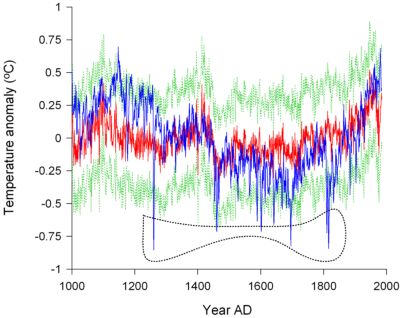
The application of general circulation models (GCMs) could improve our understanding of climate forcing. Furthermore, longer climate records spanning a wider range of climate states could help in assessing the skill of the models for simulating climates different from the present. We first attempt to find a way to combine proxy records which are affected by different seasonal temperatures, and then present a large-scale temperature reconstruction over the last millennium for China by combining the Beijing stalagmite layer series and the Qilian tree ring sequence to compare with the GCM-based ECHO-G simulated millennial temperature record for China. The correlation coefficient between the simulated and the reconstructed temperature records is 0.61 based on a 31-year running mean (exceeding P < 0.01). An asymmetrical V-like low-frequency variation shown both by the combined proxy record and the simulated series is the major long-term pattern in the last millennial temperature in China, suggesting that solar irradiance as well as greenhouse gases could explain much of the low-frequency variations in the climate. However, there still exist high-frequency discrepancies between the two time series, which may be due to (1) the overestimated climatic effect of volcanoes within the GCM and/or (2) proxies which are not sensitive enough to respond to the volcanic eruptions. Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
|
Contact
Related Articles
Reference
|
-
SIMSSecondary Ion Mass Spectrometer Laboratory
-
MC-ICPMSMultiple-collector ICPMS Laboratory
-
EM & TEMElectron Microprobe and Transmission Electron Microscope Laboratory
-
SISolid Isotope Laboratory
-
StIStable Isotope Laboratory
-
RMPARock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis
-
AAH40Ar/39Ar & (U-Th)/He Laboratory
-
EMLElectron Microscopy Laboratory
-
USCLUranium Series Chronology Laboratory
-
SASeismic Array Laboratory
-
SEELaboratory of Space Environment Exploration Laboratory
-
PGPaleomagnetism and Geochronology Laboratory
-
BioMNSFrance-China Bio-mineralization and Nano-structure Laboratory

 Print
Print Close
Close