Vice Professor JIANG Wenying and her team present pollen records from six sites across Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP), with the objective of identifying the natural vegetation types since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) and to suggest suitable plant types for vegetation restoration under global warming conditions.
According to their pollen records, priority should be given to herbs (especially the Poaceae and Asteraceae families), rather than trees or shrubs, in current and future greening programmes. Only in the deep valleys, with very thin loess and the riparian zones of large rivers, should some trees and shrubs be considered as candidate species. To combine ecological restoration with economic growth, Juglans, Corylus and some medicinal plants (e.g. Selaginella sinensis) should also serve as useful candidate species for the south-eastern Loess Plateau.
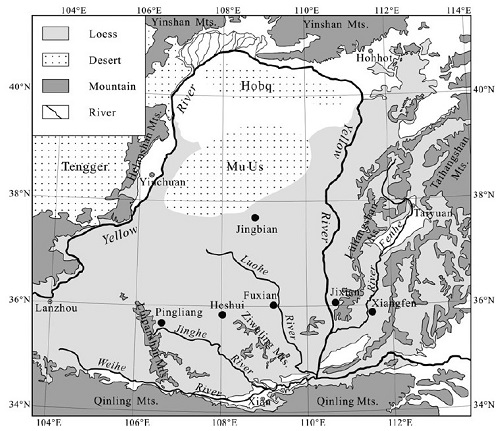
Fig. 1. Map showing the study sites (solid circles) and the distribution of loess in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. (Image by JIANG)
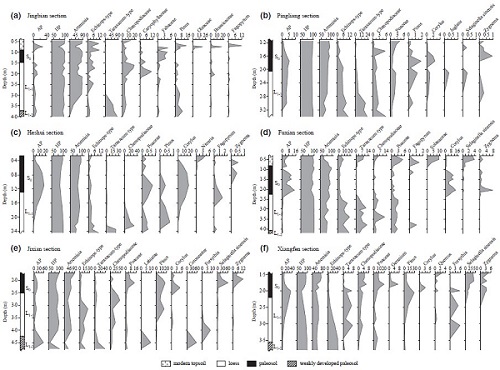
Fig. 2. Pollen percentage diagrams for major pollen types and stratigraphic columns. (Image by JIANG)
Jiang et al. Chinese Loess Plateau vegetation since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for vegetation restoration. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 50: 440-448 (Download Here)