Ph.D. student SUN Jing and Vice Professor LIU Chuanzhou present detailed in-situ trace-element and Sr-isotope analyses of clinopyroxene in the mantle xenoliths from Hebi, North China Craton (NCC).
The results confirm the existence of Arhcean mantle relics beneath the Hebi area during the Cenozoic. Clinopyroxene in the Hebi mantle xenoliths shows strong enrichment in LILEs (e.g., Th, U and LREE), but depletions in both HREE and HFSEs (e.g., Nb, Ta, Zr and Hf), which suggests that the Hebi mantle xenoliths have been metasomatized by carbonatitic melts. Strontium isotopes in clinopyroxene have been determined in-situ in 13 samples, giving 87Sr/88Sr ratios of 0.70309–0.70556, which are lower than the bulk-rock values of the Paleozoic mantle xenoliths.
Therefore, they suggest that clinopyroxenes in the Hebi mantle xenoliths crystallized from metasomatic melts. However, the metasomatic process has not significantly disturbed the Os isotope ages of the Hebi mantle xenoliths.
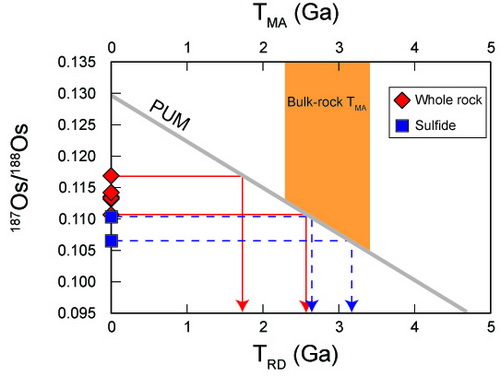
Fig. 1. TRD and TMA ages of the Hebi mantle xenoliths. (Image by SUN)
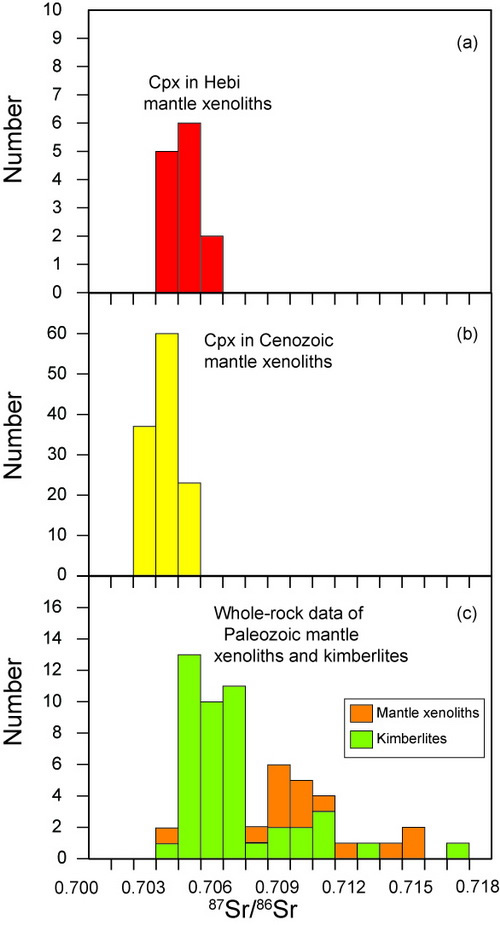
Fig. 8. Histogram of 87Sr/86Sr ratios. (Image by SUN)
Sun et al. Metasomatic origin of clinopyroxene in Archean mantle xenoliths from Hebi, North China Craton: Trace-element and Sr-isotope constraints. Chemical Geology. 2012, 328:123-136 (Download Here)