Vice Professor TU Xinbin and his team date faults and estimate surface uplift and erosion rates in the northern margin of Dabie Mountains, China by using the K-Ar dating method.
They show effective and convincing evidences for authigenic illite in fault gouge. The characteristics of the authigenic illite reveal that the host rocks were under near-surface environment during fault activities. The result indicates fault movement in Late Cretaceous in the northern margin of Dabie Mountains orogenic belt. According to the absolute timing, the uplift and erosion rates of the northern margin of Dabie Mountains are also estimated.
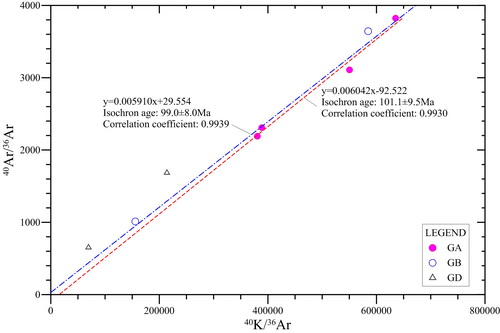
Fig. 1 K–Ar isochron age analysis. (Image by TU)
Tu et al. Dating of faults and estimation of surface uplift and erosion rates in the northern margin of Dabie Mountains, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 2012, 56: 72–76 (Download Here)