Postdoctor TANG Dongmei and Professor QIN Kezhang research the role of crustal contamination and the addition of crustal sulfur and its degree on the Tulaergen, Huangshandong, Xiangshan, Baishiquan and Tianyu Permian magmatic sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang using available trace elements and Re-Os and S isotope geochemical evidence.
They propose a two-stage crustal contamination model of the Tulaergen, Xiangshan, Tianyu, and Baishiquan intrusions. However, the Huangshan intrusion, which has the highest degree of crustal contamination, likely experienced only single-stage upper crustal contamination (~14.2%). The addition of crustal S appears to be directly related to triggering S saturation in these deposits. According to a simple S isotopic modeling calculation, 11%, 2.9%, 1.2% and 2.1% of the crustal sulfur addition into the parental magma would be required to form the Tianyu, Baishiquan, Xiangshan, and Tulaergen deposits, respectively.
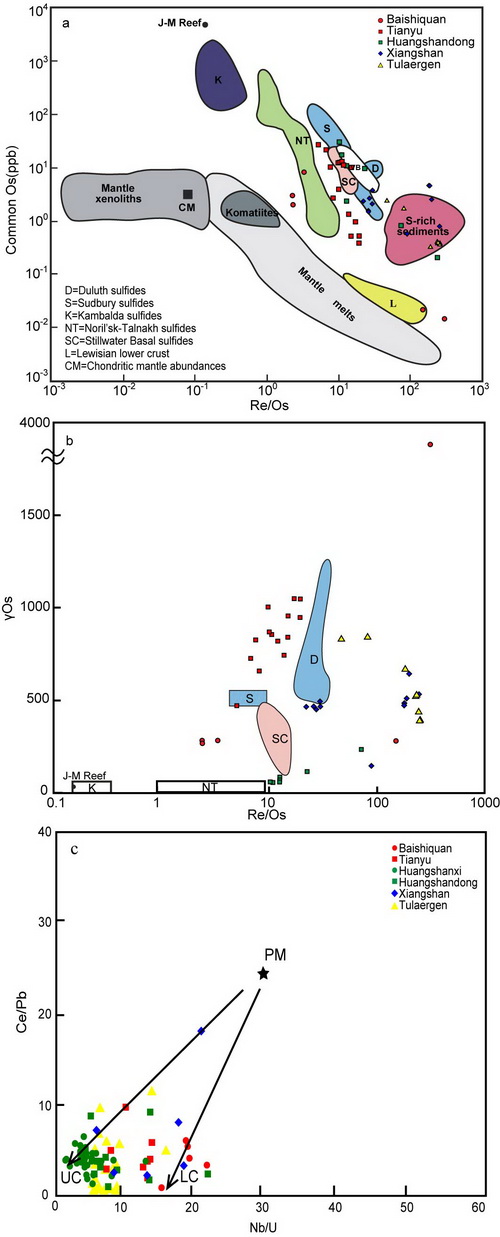
Fig.1 correlation diagrams from magmatic sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan and Central Tianshan. (Image by TANG)
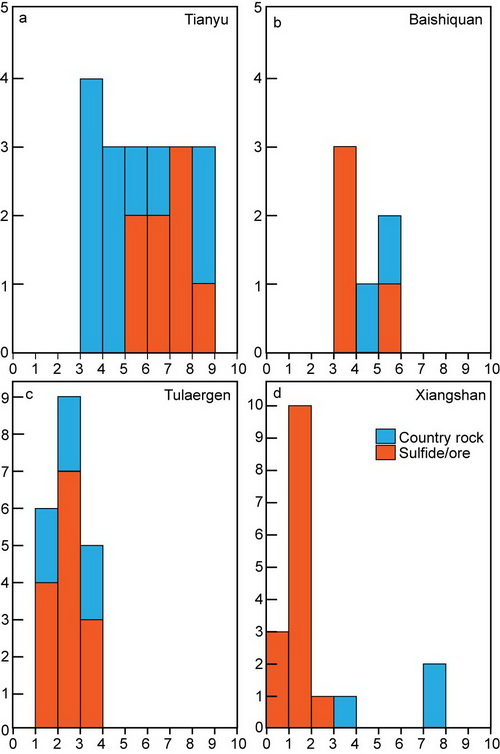
Fig. 2 Sulfur frequency chart of country rocks and sulfide from Eastern Tianshan and Central Tianshan magmatic sulfide deposits. (Image by TANG)
Tang et al. The role of crustal contamination in the formation of Ni-Cu sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang, Northwest China: Evidence from trace element geochemistry, Re-Os, Sr-Nd, zircon Hf-O, and sulfur isotopes. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 2012, 49:145-160 (Download Here)