Vice Professor SHEN Ping and her team report SIMS U–Pb zircon, elemental and Nd–Sr–Pb isotopic data for the volcanic rocks and their subvolcanic units from the Xiemisitai Mountains in the West Junggar Region (Xinjiang, China), aiming to determine their ages, source regions and tectonic setting.
These geochemical and geochronological features suggest that the Xiemisitai volcanic rocks and their subvolcanic units derived from a mantle wedge significant mixed by subducted material (EMI) in a subduction zone. They also indicate significant involvement of Neoproterozoic primitive crust in the formation of the Xiemisitai magmatic arc. These rocks are associated with a Late Silurian–Early Devonian southward subduction of the oceanic lithosphere in the northern West Junggar Region. This gives rise to an EW-trending Boshchekul-Chingiz volcanic arc and associated metallogenic belt in the northern West Junggar Region and adjacent Kazakhstan.
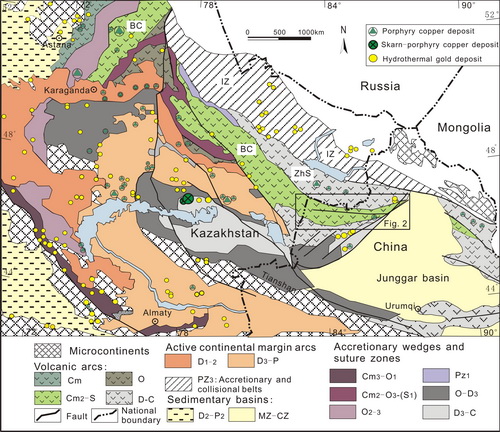
Fig. 1. Generalized geological map of the northern West Junggar Region. (Image by SHEN)
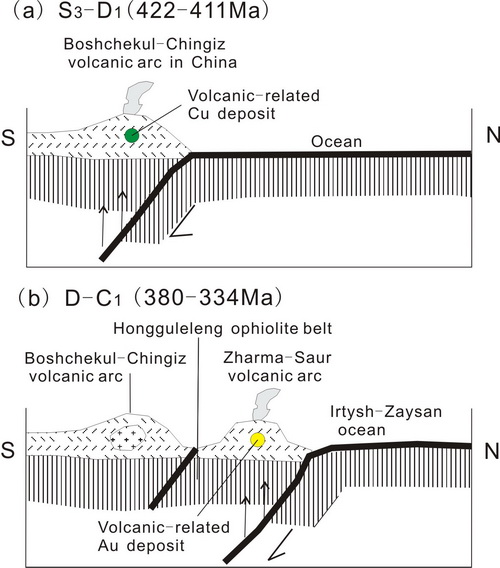
Fig. 2. Cartoon showing the evolution of geodynamic setting in the northern West Junggar Region, Xinjiang. (Image by SHEN)
Shen et al. Northwestern Junggar Basin, Xiemisitai Mountains, China: A geochemical and geochronological approach. Lithos. 2012, 140–141: 103-118 (Download Here)