Ph. D. student HE Maosheng and his teacher LIU Libo explore evidence for the electrodynamic coupling and the ionospheric signatures of direct penetration of tides to evaluate the contributions from the main processes.
They investigate the wave‐4 structure by decomposing it into interhemispheric symmetric and antisymmetric components by using F2‐layer peak density (NmF2) and the peak height (hmF2) extracted from the COSMIC data set.
Their results indicate that the generally accepted mechanism of DE3 modulation of E region dynamo only accounts for the daytime symmetric components, while the antisymmetric components could be explained well in the terms of the SE2 (semidiurnal eastward‐propagating with zonal wave number‐2) tide in transequatorial neutral wind. Surprisingly, the antisymmetric component dominates the wave‐4 structure in hmF2 during nighttime, suggesting the SE2 transequatorial wind is the leading contributor to the nighttime wave‐4 structure in hmF2.
He et al. Strong evidence for couplings between the ionospheric wave-4 structure and atmospheric tides. Geophys. Res. Lett.,2011,38,L14101,DOI: 10.1029/2011GL047855 (Download Here)
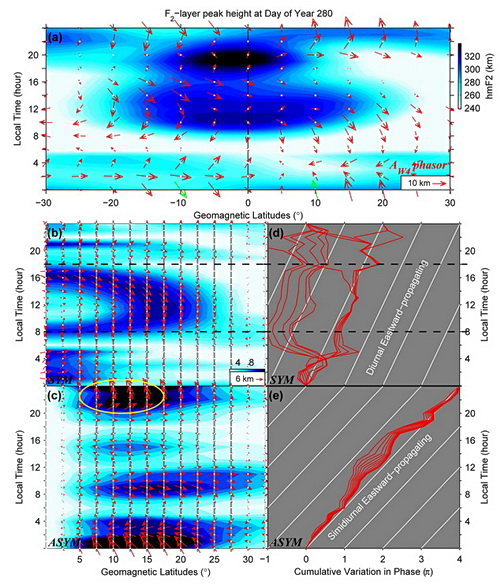
Fig.1 The results calculated from the COSMIC model described in the“Data and Methods" section. (Image by HE)