Vice Professor QING Dajun and his team investigate the natural groundwater recharge and the impact of irrigation activity on the groundwater system in the semi-arid Zhangye Basin of China.
In their paper, CFCs, together with tritium, stable isotopes, as well as electrical conductivity measurements, are used to identify and quantify irrigation water recharge in groundwater mixtures from a shallow sand aquifer in the Zhangye Basin. The objective of the study is to assess the impact of irrigation water on groundwater recharge and quality, in particular, in an arid region where evaporation exceeds precipitation through out the year to provide a better understanding of the aquifer system for improvement of river basin management.
The positive correlation between nitrate and CFC data show that contaminants are transported to the saturated zone by irrigation water. This study shows that in this semi-arid basin due to strong evaporation of infiltrating surface water and regional groundwater. Combined with a proper mixing model, however, they can provide evidences that the CFCs found in groundwater were introduced by infiltrating irrigation return flow and, therefore, reveal that human activities can produce a much localized water circulation and influence groundwater vulnerability.
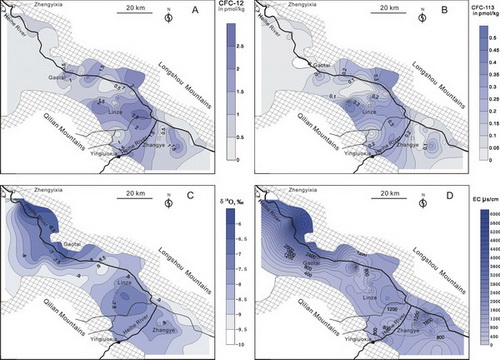
Fig.1 Plot showing distribution of CFC-12 (A), CFC-113 (B) concentrations (pmol/kg), δ18O (‰) (C) and EC (ls/cm) (D) in groundwater from the Zhangye Basin. (Image by QING)
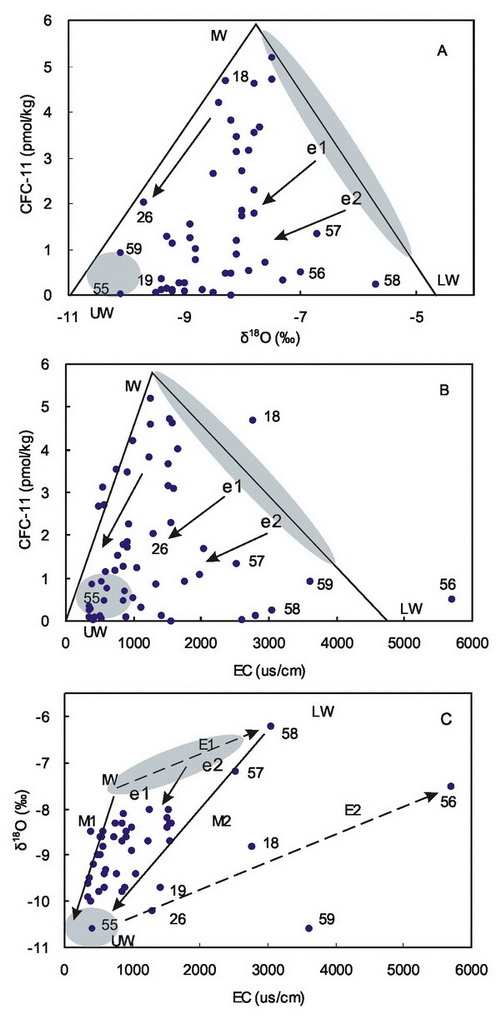
Fig.2 Relationship of δ18O, CFC-11 and EC in groundwater and river water. (Image by QING)
Qin et al. Assessing impact of irrigation water on groundwater recharge and quality in arid environment using CFCs, tritium and stable isotopes, in the Zhangye Basin, Northwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 405: 194–208(Download Here)