Postdoctor HUANG Jing and Professor CHU Xuelei study the Doushantuo cap carbonate (c. 635 Ma) in South China.
Their study illustrates that Major and trace element, including REE, concentrations of the Doushantuo cap carbonate (c. 635 Ma) in South China show enrichment in Fe, Mn and redox-sensitive elements and slightly negative Ce anomalies, indicating anoxic environments during cap carbonate precipitation.
In combination with results from other time-equivalent cap carbonates, the high Fe and Mn concentrations in the Doushantuo cap carbonate are probably from enriched Fe2+ in seawater, implying ferruginous seawater during and after the Nantuo glaciation.
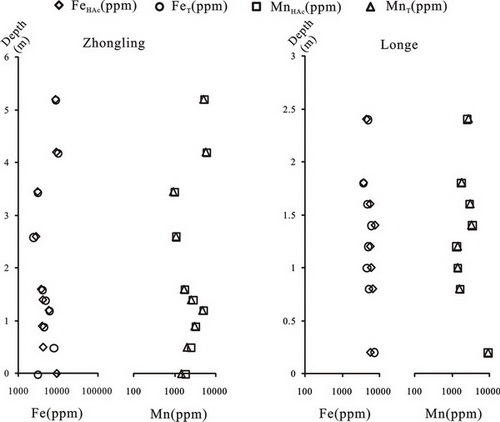
Fig. Comparison between Fe and Mn of the Doushantuo cap carbonate from the Zhongling (left) and Longe (right) sections. (Image by HUANG)
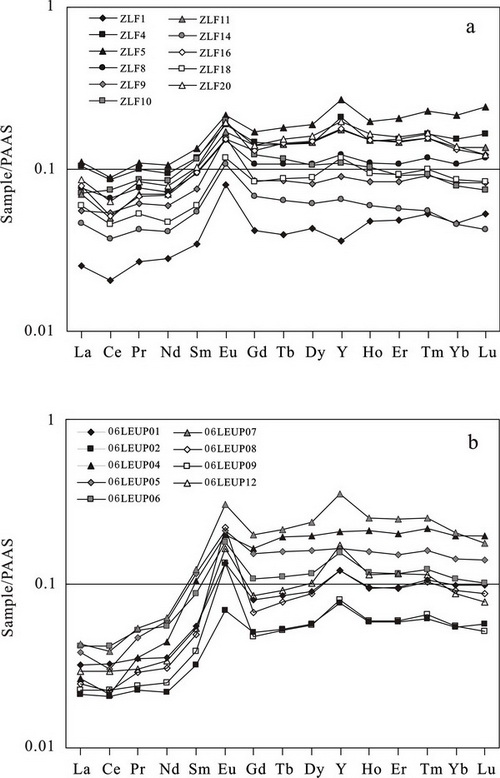
Fig. REE + Y patterns of the Doushantuo cap carbonate from Zhongling (a) and Longe (b) sections. (Image by HUANG)
Huang et al. Hydrothermal origin of elevated iron, manganese and redox-sensitive trace elements in the c. 635 Ma Doushantuo cap carbonate. Journal of the Geological Society, London, 2011, 168: 805–815(Download Here)