GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, 2009,VOL. 36, L17306, doi:10.1029/2009GL039781
Reactivation of an Archean craton: Constraints from P- and S-wave tomography in North China
Liang Zhao,Richard M. Allen,Tianyu Zheng,Shu-Huei Hung
Abstract
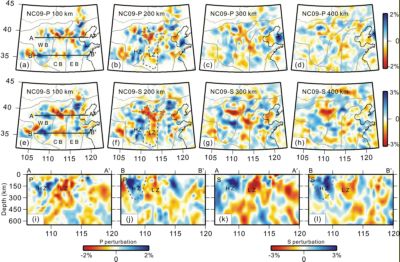
The unusual reactivation of the North China Craton (NCC) challenges the classical views concerning the strength and stability of cratonic lithosphere. By using teleseismic body-waves recorded at 250 seismic stations, this paper presents high-resolution North China Models of P- and S-wave velocity based on finite-frequency kernel tomography. Both P- and S-wave velocity models reveal that: (1) an obvious N–S trending narrow low-velocity region is located at the base of the lithosphere beneath the Central Block (CB) of the NCC, which extends to more than 500 km depth; (2) a region of high-velocity extends to more than 250–300 km depth beneath the Western Block, in contrast to the much shallower high-velocity zones beneath the CB and shallower high-velocities beneath the Eastern Block. These features suggest that warm mantle material with a source at least as deep as the transition zone, possibly a mantle plume, may be responsible for the reactivation of the NCC. The Central Block may have behaved as a sublithospheric corridor for the warm mantle material due to its pre-existing weakness.