Environmental Geology, 2009, 58: 897-911
A case study of long-term field performance of check-dams in mitigation of soil erosion in Jiangjia stream, China
Q. L. Zeng1 , Z. Q. Yue2 , Z. F. Yang1 and X. J. Zhang3
Abstract
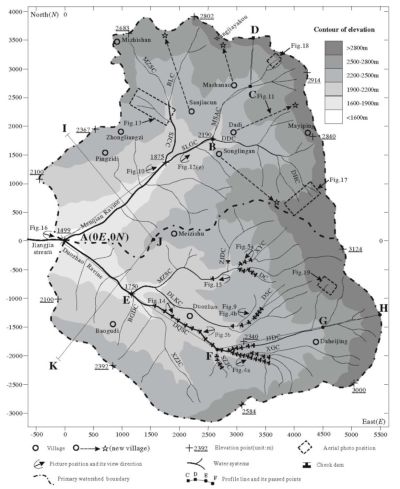
This paper examines the long-term field performance of the check-dams in mitigation of soil erosion in the Duozhao catchment of Jiangjia stream, southwest China. Since their construction between 1979 and 1982, the check-dams have been functioning effectively. The examination is made via comparisons between the environmental conditions of the Duozhao catchment with its adjacent Menqian catchment in the stream, because no check dams were constructed in the Menqian catchment. The examination is based on recent field investigations and aerial photograph analyses, and covers four aspects: (a) bed gradients of catchment channels; (b) stability of bank slopes; (c) rates of land erosion; and (d) vegetations on bank slopes. The field data demonstrate that the check-dams have had the following good functions for mitigation of soil erosion: (1) restricting the channel depth and lateral erosions, (2) protecting the channel erosion base, (3) reducing the bed gradients of debris-flow channels, (4) fixing the channel bed, (5) stabilizing the bank slopes, as well as (6) facilitating the growth of vegetations.
Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1570-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
|